Sabaton Index updates; through March 2024
Since the last update, Sabaton released a bunch of new lyric videos, some new history videos, and three videos of full albums. A couple of the history videos relate to multiple songs, so those will appear multiple times in the list. The SabatonIndex is updated with links to that new content.
LDraw Parts Library 2024-01 - Packaged for Linux
LDraw.org maintains a library of Lego part models upon which a number of related tools such as LeoCAD, LDView and LPub rely.
I packaged the 2024-01 parts library for Fedora 39 to install to /usr/share/ldraw; it should be straight-forward to adapt to other distributions.
The *.noarch.rpm files are the ones to install, and the .src.rpm contains everything so it can be rebuilt for another rpm-based distribution.
ldraw_parts-202401-ec1.fc39.src.rpm
ldraw_parts-202401-ec1.fc39.noarch.rpm
ldraw_parts-creativecommons-202401-ec1.fc39.noarch.rpm
ldraw_parts-models-202401-ec1.fc39.noarch.rpm
See also LDrawPartsLibrary.
LDraw Parts Library 2023-07 - Packaged for Linux
LDraw.org maintains a library of Lego part models upon which a number of related tools such as LeoCAD, LDView and LPub rely.
I packaged the 2023-07 parts library for Fedora 39 to install to /usr/share/ldraw; it should be straight-forward to adapt to other distributions.
The *.noarch.rpm files are the ones to install, and the .src.rpm contains everything so it can be rebuilt for another rpm-based distribution.
ldraw_parts-202307-ec1.fc39.src.rpm
ldraw_parts-202307-ec1.fc39.noarch.rpm
ldraw_parts-creativecommons-202307-ec1.fc39.noarch.rpm
ldraw_parts-models-202307-ec1.fc39.noarch.rpm
See also LDrawPartsLibrary.
LDraw Parts Library 2023-06 - Packaged for Linux
LDraw.org maintains a library of Lego part models upon which a number of related tools such as LeoCAD, LDView and LPub rely.
I packaged the 2023-06 parts library for Fedora 38 to install to /usr/share/ldraw; it should be straight-forward to adapt to other distributions.
The *.noarch.rpm files are the ones to install, and the .src.rpm contains everything so it can be rebuilt for another rpm-based distribution.
ldraw_parts-202306-ec1.fc38.src.rpm
ldraw_parts-202306-ec1.fc38.noarch.rpm
ldraw_parts-creativecommons-202306-ec1.fc38.noarch.rpm
ldraw_parts-models-202306-ec1.fc38.noarch.rpm
See also LDrawPartsLibrary.
Sabaton Index updates; through October 2023
Sabaton released a bunch of new lyric videos and some new history videos. The SabatonIndex is updated with links to that new content.
Heat-set threaded insert tooling box lid
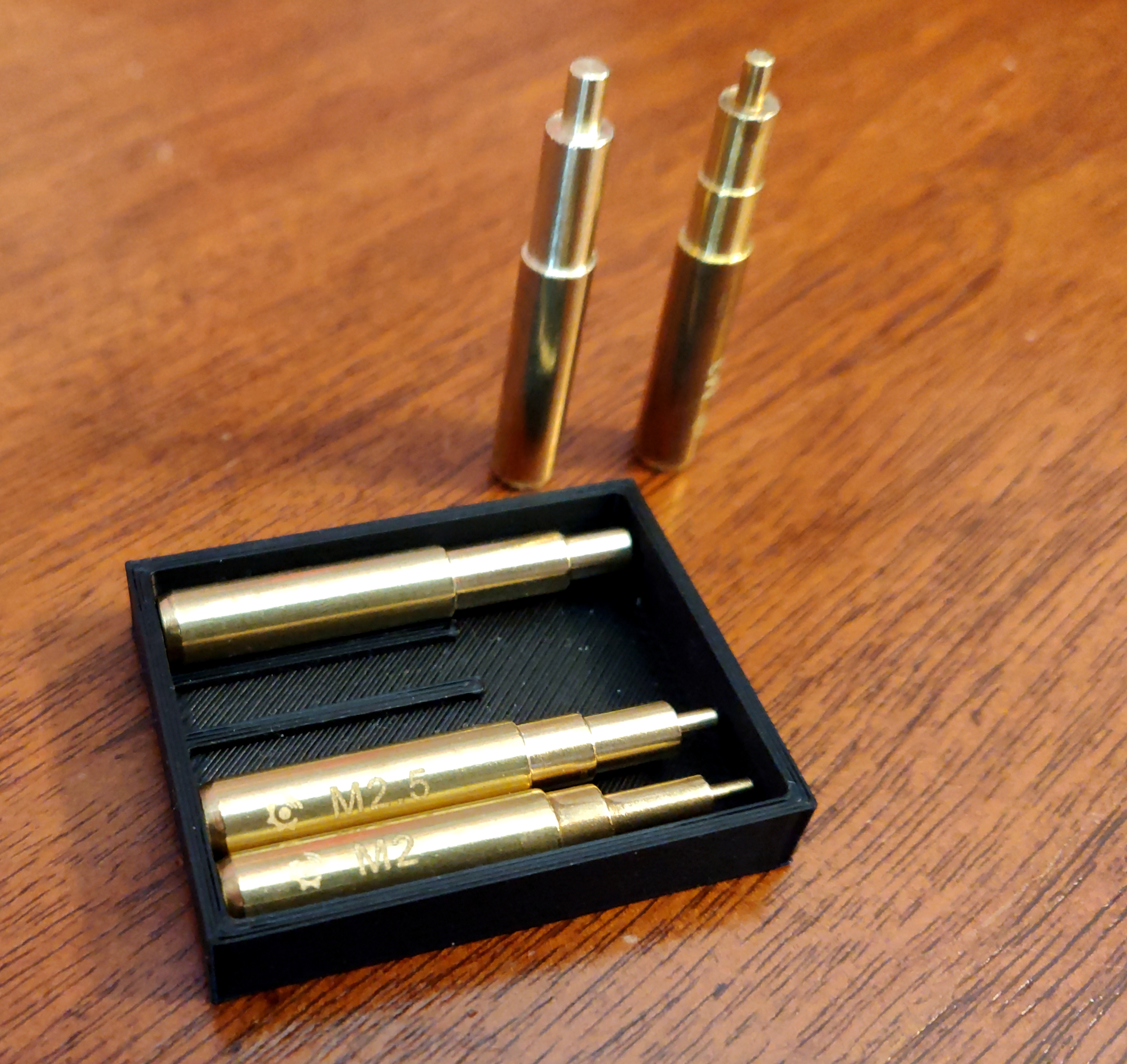
I recently discovered heat-set threaded inserts. These little bits of brass provide a way to use bolts in 3D-printed plastic parts.
The idea is that you create a plastic part with a slightly-undersized hole where the insert will go, and then using a soldering iron with a specialized tip, you heat the insert, which softens the plastic enough that you can press it into the part. Once the plastic cools, the insert is firmly embedded in the part. The inserts have internal threads which a machine screw / bolt can be screwed into. They have sharp teeth features at opposing angles on the outside, so they remain firmly embedded in the part and can't themselves unscrew.
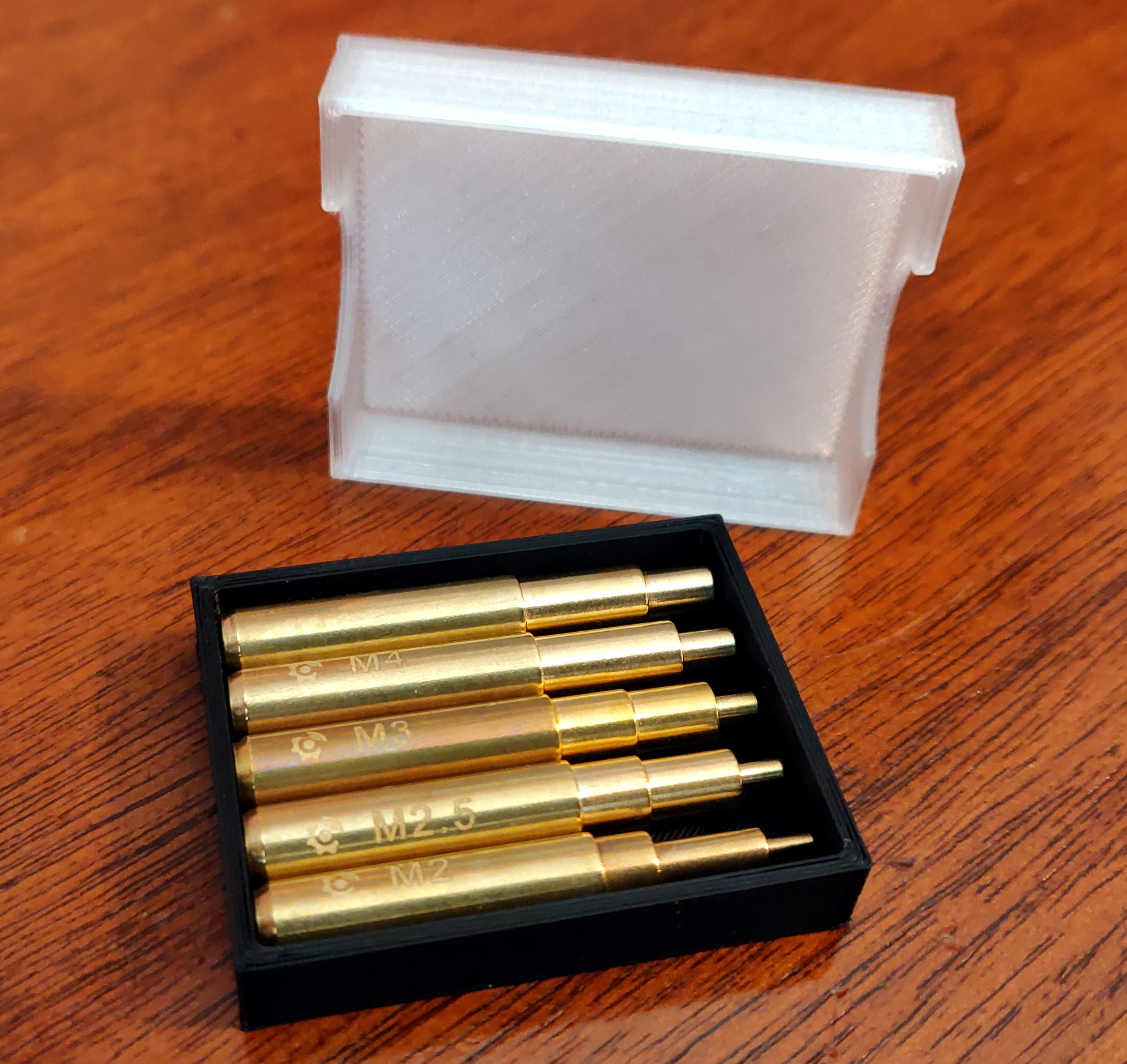
I bought a set of soldering iron tips for this purpose from Virtjoule (via Amazon). The set of brass tips came in a plastic tray which had obviously been 3D-printed.
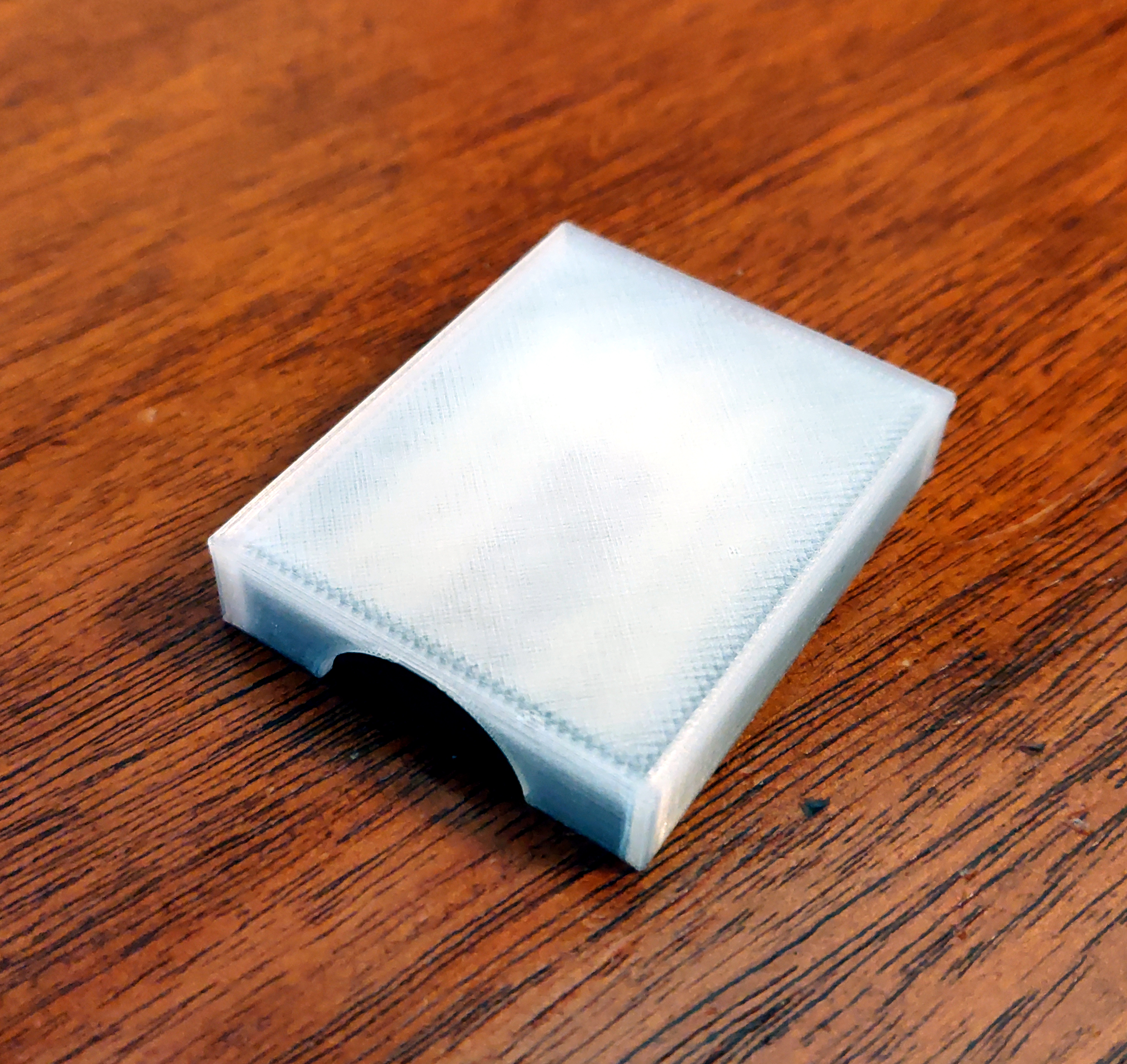
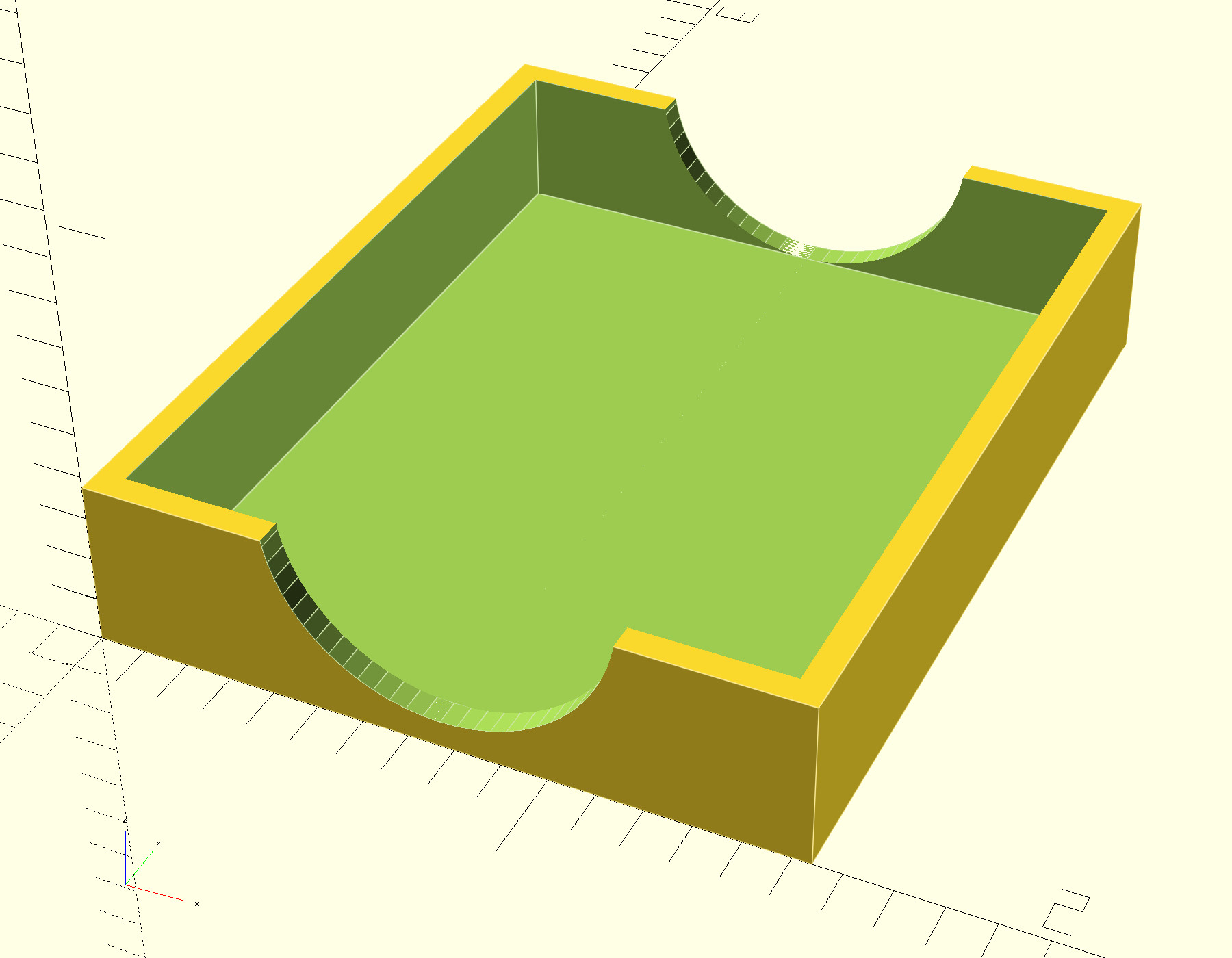
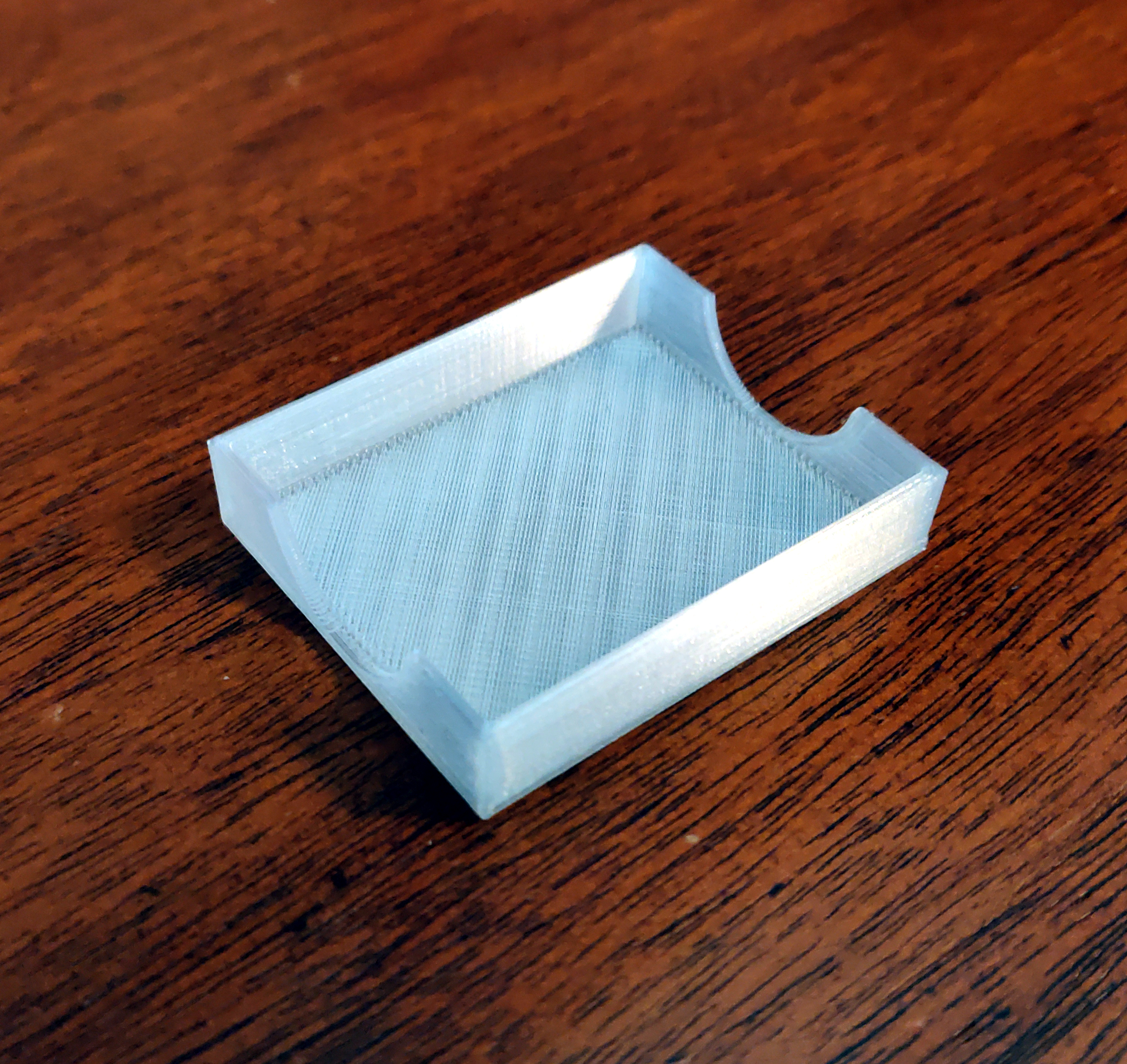
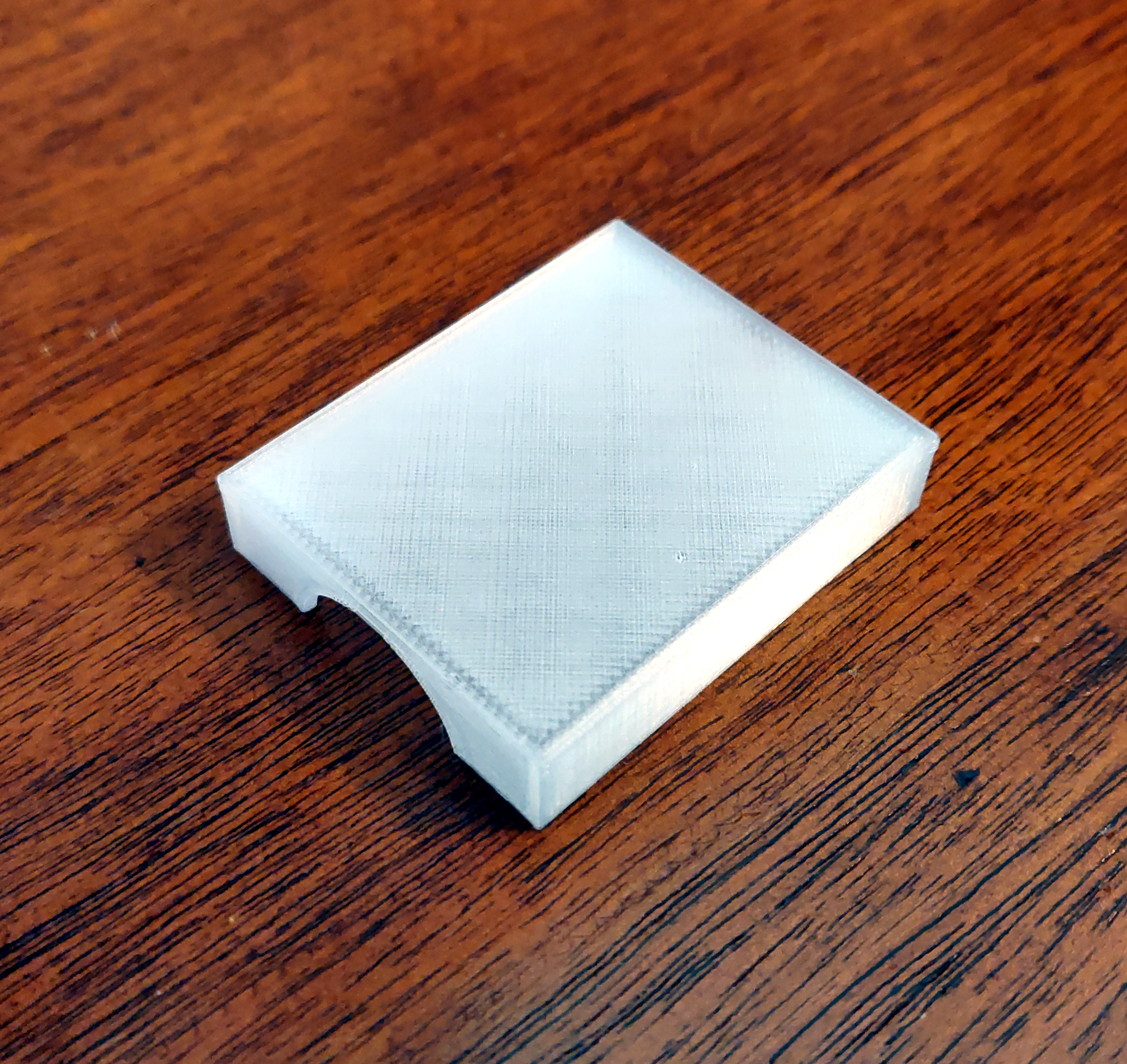
But there was no lid for the tray. So I threw together a 3D model of a lid for it (OpenSCAD, STL)
and printed it in "transparent" PLA.
That fits nicely and helps to keep the set of tips together:
Being able to quickly create a lid for a box is not something I had anticipated doing with a 3D printer, but in retrospect, it's an amazingly obvious application.
And then there's the intriguing aspect that it's useful to a business creating packaging for a specialty product. In this case, the US-based company is in a business where they are applying 3D-printed parts, and are selling a tool they themselves created and use. So they've found an additional use of infrastructure they already had, and a market for a product they had created for their own use. I think that's really neat.
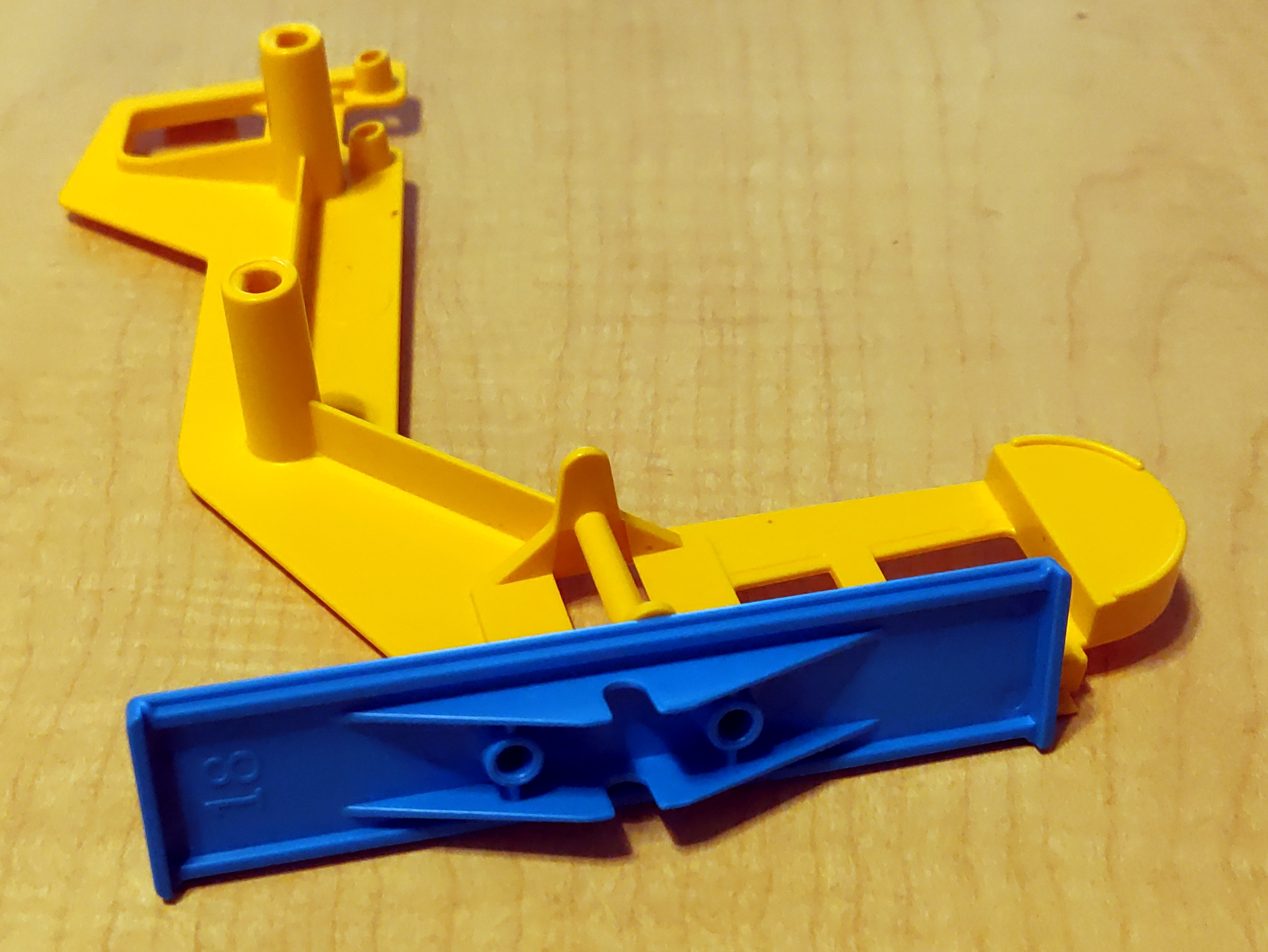
Mouse Trap replacement seesaw
There are some tools you figure will be useful, but it is difficult to really justify investing in them before you have them. And then you get it anyway, and discover how much more useful it is than you envisioned. Getting a 3D printer was that sort of experience for me; I knew I'd find it useful, but I hadn't realized just how useful. Using OpenSCAD and some calipers, I have managed to create replacement parts or useful gizmos that would not have occurred to me prior to owning a 3D printer.
Here is just one example.
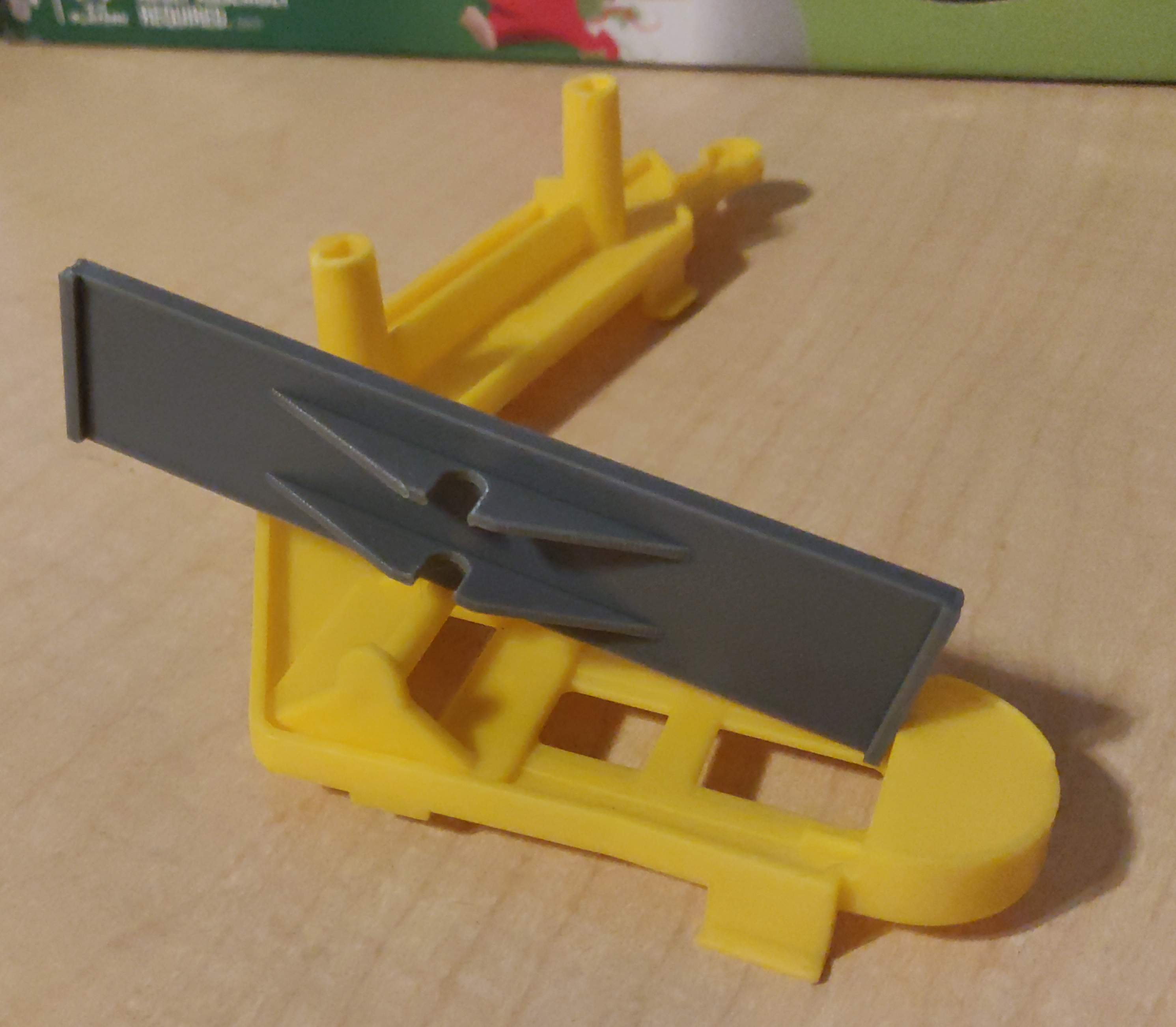
A friend of my wife had Mouse Trap, a kids' board game built around a Rube Goldberg contraption.
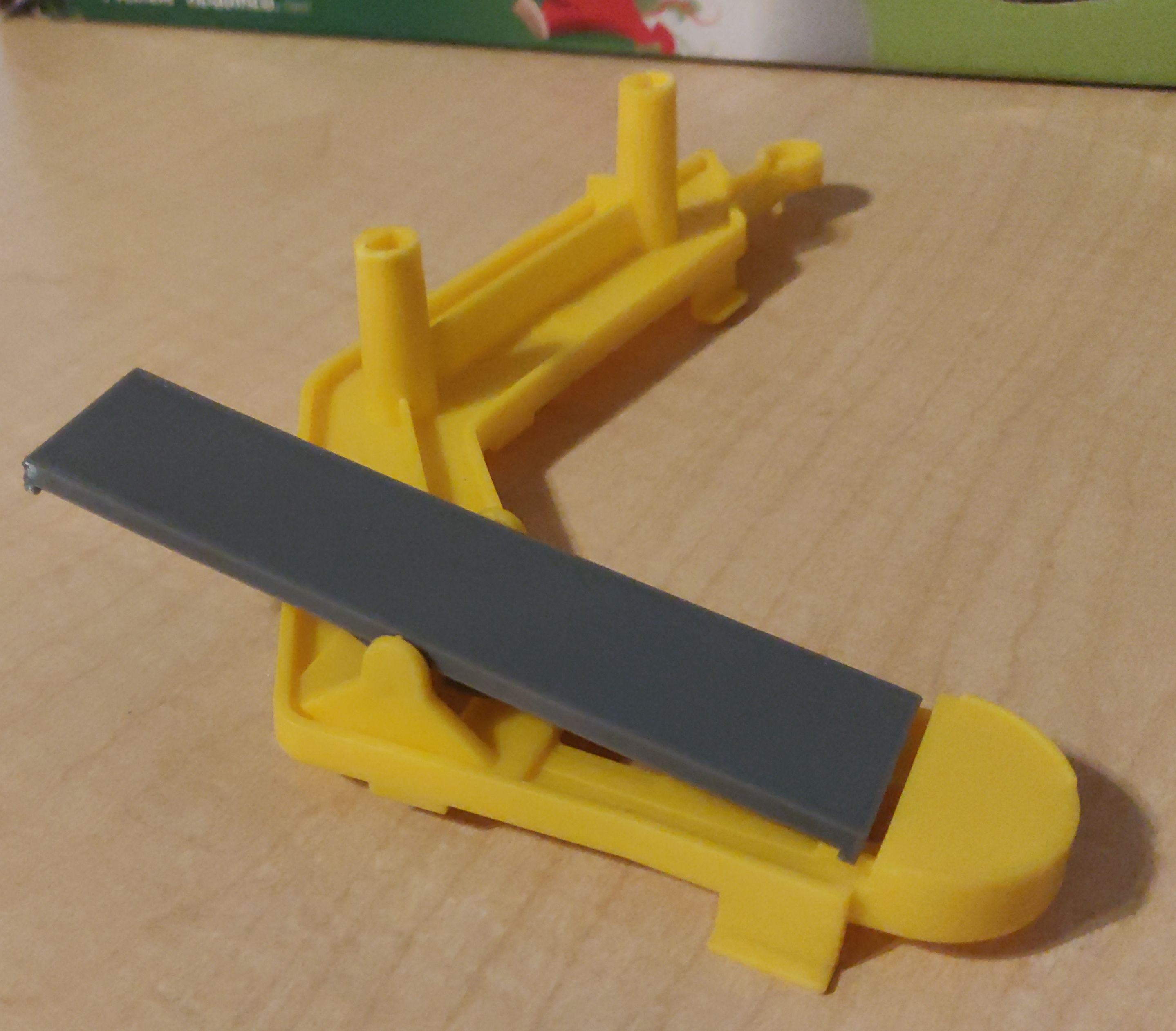
Unfortunately, she had lost the seesaw piece, which meant that the contraption could not work.
As it so happened, we also had the game, though it did have some differences.
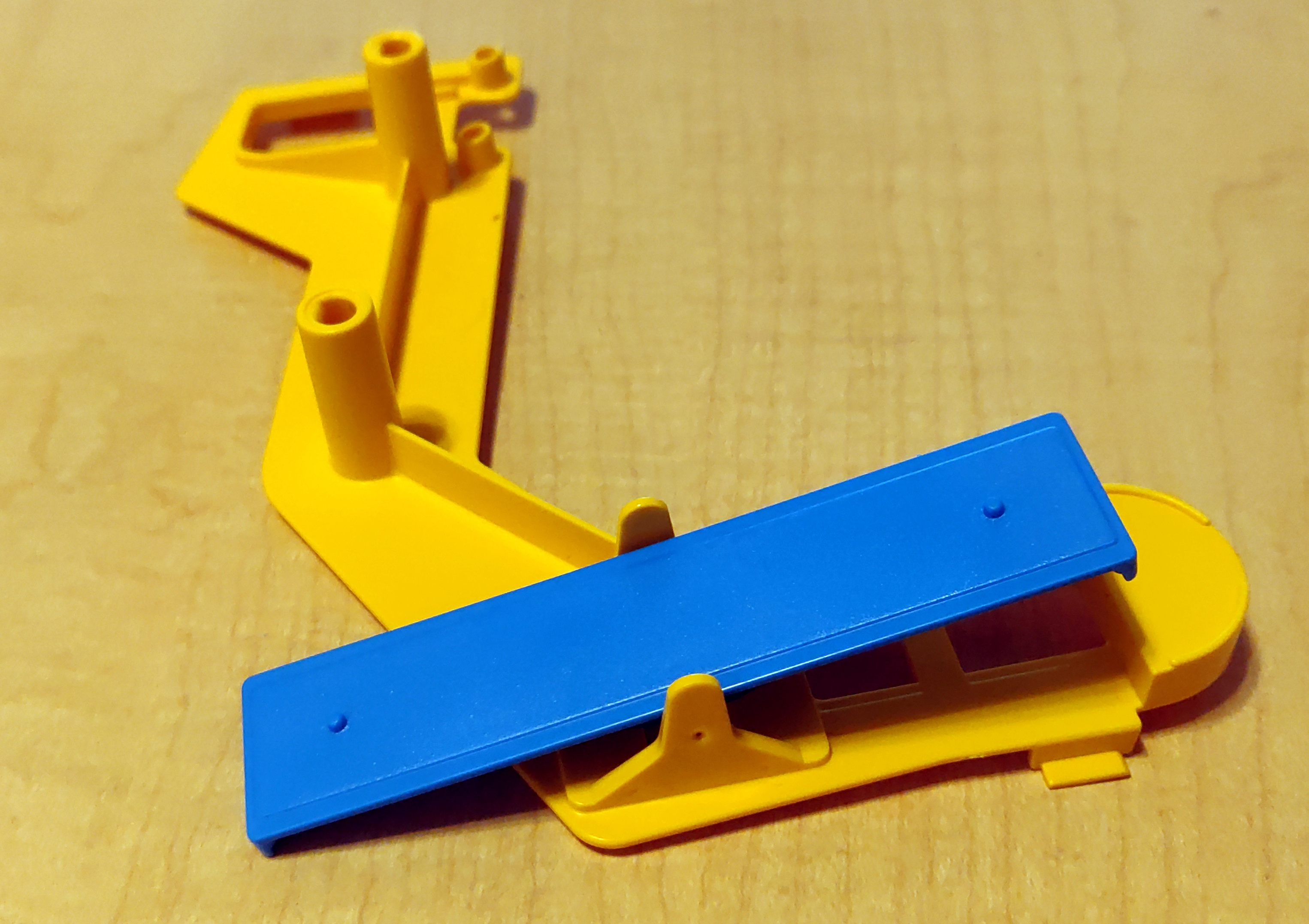
The seesaw from our game still worked with hers.
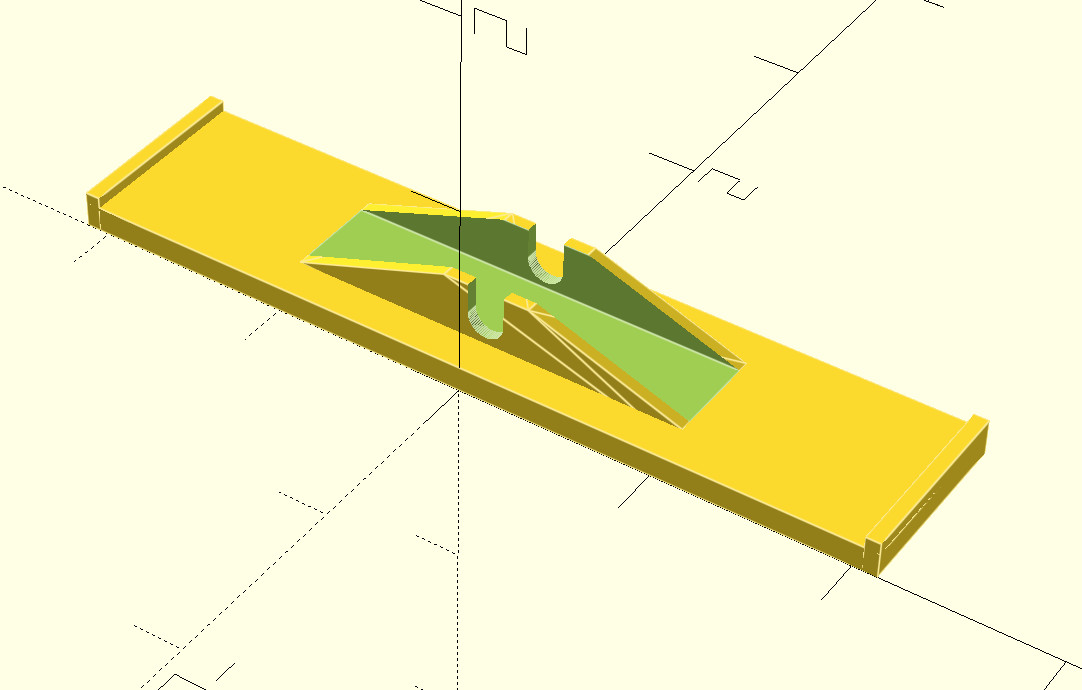
So I grabbed my calipers, and threw together a quick approximation of our seesaw in OpenSCAD,
and printed it out.
The resulting seesaw, though not as brightly colored as the rest of the game, did work, and fixed her game.
If you want to print your own, here are the OpenSCAD model and the STL.
Sabaton Index updates; through July 2023
Sabaton released a few new lyric videos and a couple of new history videos. The SabatonIndex is updated with links to that new content.
LDraw Parts Library 2023-03 - Packaged for Linux
LDraw.org maintains a library of Lego part models upon which a number of related tools such as LeoCAD, LDView and LPub rely.
I packaged the 2023-03 parts library for Fedora 36 to install to /usr/share/ldraw; it should be straight-forward to adapt to other distributions.
The *.noarch.rpm files are the ones to install, and the .src.rpm contains everything so it can be rebuilt for another rpm-based distribution.
ldraw_parts-202303-ec1.fc36.src.rpm
ldraw_parts-202303-ec1.fc36.noarch.rpm
ldraw_parts-creativecommons-202303-ec1.fc36.noarch.rpm
ldraw_parts-models-202303-ec1.fc36.noarch.rpm
See also LDrawPartsLibrary.
Grid-based Tiling Window Management, Mark III, aka QuickGridZones
With a laptop and a 4K monitor, I wind up with a large number of windows scattered across my screens. The general disarray of scattered and randomly offset windows drives me nuts.
I've done some work to address this problem before (here and here), which I had been referring to as "quicktile". But that's what KDE called its implementation that allowed snapping the window to either half of the screen, or to some quarter. On Windows, there's a Power Tool called "Fancy Zones" that also has a few similarities. In an effort to disambiguate what I've built, I've renamed my approach to "Quick Grid Zones".
Since the last post on this, I've done some cleanup of the logic and also ported it to work on Windows.
This isn't a cross-platform implementation, but rather three implementations with some structural similarities, implemented on top of platform-specific tools.
- Linux KDE - KDE global shortcuts that call a Python script using xdotool, wmctrl, and xprop
- Mac OS - a lua script for Hammerspoon
- Windows - an AutoHotKey2 script
Simple demo of running this on KDE:
Grab the local tarball for this release, or check out the QuickGridZones project page.
 rss
rss